Marbled cat
| Marbled cat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A marbled cat in Danum Valley, Borneo | |
Conservation status | |
CITES Appendix I (CITES)[2] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Felinae |
| Genus: | Pardofelis |
| Species: | P. marmorata[1] |
| Binomial name | |
| Pardofelis marmorata[1] (Martin, 1836) | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
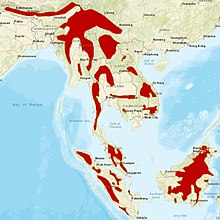 | |
| Distribution of marbled cat, 2016[2] | |
The marbled cat (Pardofelis marmorata) is a small wild cat native from the eastern Himalayas to Southeast Asia, where it inhabits forests up to an elevation of 2,500 m (8,200 ft). As it is present in a large range, it has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List since 2015.[2]
The marbled cat is closely related to the Asian golden cat (Catopuma temminckii) and the bay cat (C. badia), all of which diverged from other felids about 9.4 million years ago.[3]
Characteristics
The marbled cat is similar in size to a domestic cat, but has rounded ears and a very long tail that is as long as the cat's head and body. The ground colour of its long fur varies from brownish-grey to ochreous brown above and greyish to buff below. It is patterned with black stripes on the short and round head, on the neck and back. On the tail, limbs and underbelly it has solid spots. On the flanks it has irregular dark-edged blotches that fuse to dark areas and look like a 'marbled' pattern. Its paws are webbed between the digits and are completely sheathed.[4] Its coat is thick and soft. Spots on the forehead and crown merge into narrow longitudinal stripes on the neck, and irregular stripes on the back. The legs and underparts are patterned with black dots, and the tail is marked with black spots proximally and rings distally. It has large feet and unusually large canine teeth, resembling those of the big cats, although these appear to be the result of parallel evolution. Marbled cats range from 45 to 62 cm (18 to 24 in) in head-body length with a 35 to 55 cm (14 to 22 in) long and thickly furred tail that indicates the cat's adaptation to an arboreal lifestyle, where the tail is used as a counterbalance. Recorded weights vary between 2 and 5 kg (4.4 and 11.0 lb).[5]
Distribution and habitat
The marbled cat occurs along the eastern Himalayan foothills and in tropical Indomalaya eastward into southwest China, and on the islands of Sumatra and Borneo. It is primarily associated with moist and mixed deciduous-evergreen tropical forests. Its distribution in India is confined to the north-eastern forests.[2]
In eastern Nepal, a marbled cat was recorded for the first time in January 2018, outside a protected area in the Kangchenjunga landscape at an altitude of 2,750 m (9,020 ft).[6]
In northeast India, marbled cats were recorded in Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary, Dampa and Pakke Tiger Reserves, Balpakram-Baghmara landscape and Singchung-Bugun Village Community Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh between January 2013 and March 2018.[7]
In Bhutan, it has been recorded in Royal Manas National Park, and in broadleaved and mixed conifer forests at elevations up to 3,810 m (12,500 ft) in Jigme Dorji National Park and Wangchuck Centennial National Park.[8][9][10]
In Thailand, it was recorded in a hill evergreen bamboo mixed forest in Phu Khieu Wildlife Sanctuary.[11]
In Borneo, it has also been recorded in peat swamp forest.[12] The population size of the marbled cat is not well understood. Few records were obtained during camera-trapping surveys throughout much of its range. In three areas in Sabah, the population density was estimated at 7.1 to 19.6 individuals per 100 km2 (39 sq mi), an estimate that may be higher than elsewhere in the cat's range.[13] In Kalimantan, marbled cats were recorded in mixed swamp forest and tall interior forest at altitudes below 20 m (66 ft) in the vicinity of Sabangau National Park between 2008 and 2018.[14]
Behaviour and ecology
Marbled cats recorded in northeastern India and Kalimantan on Borneo were active by day.[7][14]
The first-ever radio-tracked marbled cat had an overall home range of 5.8 km2 (2.2 sq mi) at an elevation of 1,000 to 1,200 m (3,300 to 3,900 ft) and was active primarily during nocturnal and crepuscular times.[11] Marbled cats recorded in northeast India were active during the day with activity peaks around noon.[7]
Forest canopies probably provide the marbled cat with much of its prey: birds, squirrels and other rodents, and reptiles.[5] In the Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park, a marbled cat was observed in a dense forest patch in an area also used by siamang.[15] In Thailand, one individual has been observed in Phu Khieo Wildlife Sanctuary preying on a Phayre's leaf monkey.[16]
A few marbled cats have been bred in captivity, with gestation estimated to be 66 to 82 days. In the few recorded instances, two kittens were born in each litter, and weighed from 61 to 85 g (2.2 to 3.0 oz). Their eyes open at around 12 days, and the kittens begin to take solid food at two months, around the time that they begin actively climbing. Marbled cats reach sexual maturity at 21 or 22 months of age, and have lived for up to 12 years in captivity.[5]
Threats
The primary threat to the marbled cat is loss and degradation of forest as it depends on large tracts of intact forest.[17] Forest loss is continuing across its range due to logging and expansion of human settlements and agriculture.[2] Indiscriminate snaring is prevalent throughout much of its range, and also likely poses a major threat. It is valued for its skin, meat, and bones, but infrequently observed in the illegal Asian wildlife trade.[2] During a survey in the Lower Subansiri District of Arunachal Pradesh, a marbled cat was encountered that had been killed by a local hunter for a festival celebrated by the indigenous Apatani people in March and April every year. The dead cat was used in a ceremony, and its blood was sacrificed to the deity for goodwill of their family and for ensuring a good harvest, protection from wildlife, disease and pest.[18]
Conservation
Pardofelis marmorata is included in CITES Appendix I and protected over parts of its range. Hunting is prohibited in Bangladesh, Cambodia, Yunnan, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, and Thailand. Hunting is regulated in Laos and Singapore. In Bhutan and Brunei, the marbled cat is not legally protected outside protected areas. No information about protection status is available from Cambodia and Vietnam.[19]
Taxonomy
Felis marmorata was the scientific name proposed by William Charles Linnaeus Martin in 1836 for a skin of a male marbled cat from Java or Sumatra.[20] Felis longicaudata proposed by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1843 was a zoological specimen from India or Cochinchina.[21] Felis charltoni proposed by John Edward Gray in 1846 was a specimen from Darjeeling.[22] The generic name Pardofelis was proposed by Nikolai Severtzov in 1858.[23]
At present, two subspecies are recognized as valid:[24]
- P. marmorata marmorata (Martin, 1836) – from the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra and Borneo
- P. marmorata longicaudata (Blainville, 1843) – from Nepal to north of the Isthmus of Kra
Phylogeny
The marbled cat was once considered to belong to the pantherine lineage of cats.[25] But results of a phylogenetic analysis indicate that it forms an evolutionary lineage with the Asian golden cat (Catopuma temminckii) and the bay cat (C. badia) that genetically diverged about 12.77 to 7.36 million years ago. The marbled cat diverged from this lineage about 8.42 to 4.27 million years ago.[3][26]
References
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Species Pardofelis marmorata". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 542. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d e f g Ross, J.; Brodie, J.; Cheyne, S.; Datta, A.; Hearn, A.; Loken, B.; Lynam, A.J.; McCarthy, J.; Phan, C.; Rasphone, A.; Singh, P. & Wilting, A. (2016). "Pardofelis marmorata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T16218A97164299. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T16218A97164299.en. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ a b Johnson, W. E.; Eizirik, E.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Murphy, W. J.; Antunes, A.; Teeling, E. & O'Brien, S. J. (2006). "The Late Miocene Radiation of Modern Felidae: A Genetic Assessment". Science. 311 (5757): 73–77. Bibcode:2006Sci...311...73J. doi:10.1126/science.1122277. PMID 16400146. S2CID 41672825.
- ^ Pocock, R. I. (1939). "Genus Pardofelis Severtzow". The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Mammalia – Volume 1. London: Taylor and Francis. pp. 253−258.
- ^ a b c Sunquist, M. & Sunquist, F. (2002). "Marbled cat Pardofelis marmorata (Martin 1837)". Wild Cats of the World. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 373–376. ISBN 978-0-226-77999-7.
- ^ Lama, S. T.; Ross, J. G.; Bista, D.; Sherpa, A. P.; Regmi, G. R.; Suwal, M. K.; Sherpa, P.; Weerman, J.; Lama, S. S.; Thapa, M.; Poudyal, L. P. (2019). "First photographic record of marbled cat Pardofelis marmorata Martin, 1837 (Mammalia, Carnivora, Felidae) in Nepal". Nature Conservation. 32: 19−34. doi:10.3897/natureconservation.32.29740. hdl:10182/10670.
- ^ a b c Mukherjee, S.; Singh, P.; Silva, A.; Ri, C.; Kakati, K.; Borah, B.; Tapi, T.; Kadur, S.; Choudhary, P.; Srikant, S.; Nadig, S.; Navya, R.; Björklund, R.; Ramakrishnan, U. (2019). "Activity patterns of the small and medium felid (Mammalia: Carnivora: Felidae) guild in northeastern India". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 11 (4): 13432−13447. doi:10.11609/jott.4662.11.4.13432-13447.
- ^ Tempa, T.; Hebblewhite, M.; Mills, L.S.; Wangchuk, T.R.; Norbu, N.; Wangchuk, T.; Nidup, T.; Dhendup, P.; Wangchuk, D.; Wangdi, Y. & Dorji, T. (2013). "Royal Manas National Park: A hotspot for wild felids, Bhutan". Oryx. 47 (2): 207–210. doi:10.1017/s0030605312001317.
- ^ Thinley, P.; Morreale, S.J.; Curtis, P.D.; Lassoie, J.P.; Dorji, T.; Leki; Phuntsho, S. & Dorji, N. (2015). "Diversity, occupancy, and spatio-temporal occurrences of mammalian predators in Bhutan's Jigme Dorji National Park". Bhutan Journal of Natural Resources & Development. 2 (1): 19–27.
- ^ Dhendup, T. (2016). "Notes on the occurrence of Marbled Cats at high altitudes in Bhutan" (PDF). NeBIO. 7 (2): 35–37.
- ^ a b Grassman, L. I. Jr.; Tewes, M. E. (2000). "Marbled cat in northeastern Thailand". Cat News. 33: 24.
- ^ Cheyne, S. M.; Macdonald, D. W. (2010). "Marbled cat in Sabangau peat-swamp forest, Indonesian Borneo" (PDF). Cat News. 52: 11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-08-03. Retrieved 2017-12-04.
- ^ Hearn, A. J.; Ross, J.; Bernard, H.; Bakar, S. A.; Hunter, Luke T. B.; Macdonald, D. W. (2016). "The First Estimates of Marbled Cat Pardofelis marmorata Population Density from Bornean Primary and Selectively Logged Forest". PLOS ONE. 11 (3): e0151046. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1151046H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0151046. PMC 4805203. PMID 27007219.
- ^ a b Jeffers, K. A.; Adul; Cheyne, S. M. (2019). "Small cat surveys: 10 years of data from Central Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 11 (4): 13478–13491. doi:10.11609/jott.4466.11.4.13478-13491.
- ^ Morino, L. (2009). "Observation of a wild marbled cat in Sumatra". Cat News (50): 20.
- ^ Borries, C.; Primeau, Z. M.; Ossi-Lupo, K.; Dtubpraserit, S. & Koenig, A. (2014). "Possible predation attempt by a marbled cat on a juvenile Phayre's leaf monkey". Raffles Bulletin of Zoology (62): 561–565.
- ^ Hendry, A.; Amir, Z.; Decoeur, H.; Mendes, C. P.; Moore, J. H; Sovie, A.; Luskin, M. S. (January 2023). "Marbled cats in Southeast Asia: Are diurnal and semi-arboreal felids at greater risk from human disturbances?". Ecosphere. 14 (1): e4338. doi:10.1002/ecs2.4338.
- ^ Selvan, K. M.; Gopi, G. V.; Habib, B.; Lyngdoh, S. (2013). "Hunting record of endangered Marbled Cat Pardofelis marmorata in the Ziro Valley of Lower Subansiri, Arunachal Pradesh, India". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 5 (1): 3583–3584. doi:10.11609/JoTT.o3208.100.
- ^ Nowell, K. and Jackson, P. (1996). Marbled Cat Felis marmorata. in: Wild Cats. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK.
- ^ Martin, W. C. (1836). "Description of a new species of Felis". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. IV (XLVII): 107–108.
- ^ Blainville, H. M. D. (1843). "Os du squelette des Felis". Ostéographie ou description iconographique comparée du squelette et du système dentaire des cinques classes d'animaux vertébrés récents et fossils pour servir de base a la zoologie et la géologie. Volume 2: Mammifères. Carnassiers. Paris: Arthus Bertrand. pp. 1–196.
- ^ Gray, J. E. (1846). "New species of Mammalia". The Annals and Magazine of Natural History; Zoology, Botany, and Geology. 18 (118): 211−212. doi:10.1080/037454809494412.
- ^ Severtzow, M. N. (1858). "Notice sur la classification multisériale des Carnivores, spécialement des Félidés, et les études de zoologie générale qui s'y rattachent". Revue et Magasin de Zoologie Pure et Appliquée. X: 385–396.
- ^ Kitchener, A. C.; Breitenmoser-Würsten, C.; Eizirik, E.; Gentry, A.; Werdelin, L.; Wilting, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Abramov, A. V.; Christiansen, P.; Driscoll, C.; Duckworth, J. W.; Johnson, W.; Luo, S.-J.; Meijaard, E.; O’Donoghue, P.; Sanderson, J.; Seymour, K.; Bruford, M.; Groves, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Nowell, K.; Timmons, Z.; Tobe, S. (2017). "A revised taxonomy of the Felidae: The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group" (PDF). Cat News (Special Issue 11): 34−35.
- ^ Hemmer, H. (1978). "The evolutionary systematics of living Felidae: Present status and current problems". Carnivore. 1: 71–79.
- ^ Werdelin, L.; Yamaguchi, N.; Johnson, W. E.; O'Brien, S. J. (2010). "Phylogeny and evolution of cats (Felidae)". In Macdonald, D. W.; Loveridge, A. J. (eds.). Biology and Conservation of Wild Felids. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 59–82. ISBN 978-0-19-923445-5.
External links


- "Marbled cat Pardofelis marmorata". IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group.
- v
- t
- e
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Infraclass: Eutheria
- Superorder: Laurasiatheria
Feliformia ("cat-like" carnivorans) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Caniformia ("dog-like" carnivorans) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pinnipedia (seals) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||











